Modern manufacturing demands precision, efficiency, and reliability. However, in most facilities, there is a problem of the outdated systems and disintegrated processes. Industrial control & automation addresses these challenges head-on. It changes the ways that facilities are run that save money and enhance quality of output. This technology is not only good, but it is becoming a requirement of competitive advantage.
The modern world of industries demands to be integrated to facilitate solutions that are flexible. Understanding control and automation fundamentals helps facilities make informed decisions.
Understanding Industrial Control & Automation Systems
Industrial controls and automation combines hardware and software to manage facility operations. These systems monitor, control, and optimize manufacturing processes automatically. Sensors collect real-time data from equipment and production lines. Controllers process this information and make instantaneous adjustments. The outcome is a smooth running that minimally involves human intervention.
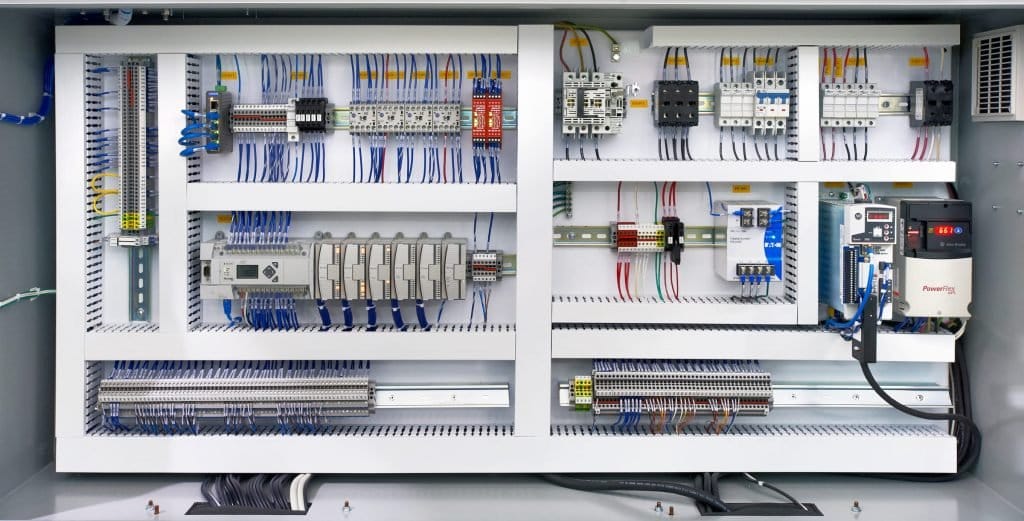
Core Components of Automation Systems
Every effective control system automation includes several critical elements. The brain of the system is the Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). They carry out control algorithms and communicate among field devices. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) provide visual feedback to the operator. The SCADA systems collect data on various points and make them centrally monitored. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) have the advantage of controlling the speed of the motor. Combined these elements form a unified working system.
Types of Control Systems
Different facilities require different approaches to industrial process control and automation system implementation. Embarkation systems control singly and individual machines and processes. Continuous process control deals with such operations as chemical mixing or refining. Production is controlled in batches of production. Sequential control involves control that takes processes through pre-defined procedures. All the types have their industrial needs.
Benefits of Integrated Industrial Control & Automation
Implementing comprehensive industrial control & automation delivers measurable advantages. First, operational efficiency increases dramatically across all departments. Energy consumption drops as systems optimize resource usage continuously. Product quality improves through consistent, repeatable processes. Labor costs decrease while worker safety significantly improves. Equipment lifespan extends through predictive maintenance capabilities.
1. Enhanced Production Efficiency
Control and automation systems eliminate bottlenecks in production workflows. Machines operate at optimal speeds without manual adjustment. Downtime reduces as systems detect problems before failures occur. Production schedules adapt automatically to changing demands. Real-time monitoring identifies inefficiencies for immediate correction. These improvements translate directly to bottom-line results.
2. Improved Safety Standards
The most important thing in an industrial setting nowadays is safety. Industrial controls and automation minimize human exposure to hazardous conditions. The systems automatically shut down on sensing hazardous situations. Access controls prevent unauthorized personnel from dangerous areas. Emergency protocols execute instantly without human decision delays. The logging will be thorough and will give safety records.
3. Cost Reduction Strategies
Financial benefits of control system automation extend beyond obvious savings. The energy management systems save 20-30% of utility costs. Reduction of waste generated by the accurate control decreases the cost of materials. The maintenance becomes proactive and not reactive, preventing expensive breakdown. The optimization of labor enables re-deployment of the staff to the value-adding activities.
Key Technologies in Modern Industrial Control & Automation
Today’s industrial control & automation leverages cutting-edge technological innovations. IoT sensors offer more details on data than ever. Artificial intelligence extracts patterns that can not be determined by people easily. Cloud computing is able to monitor or control remotely. Edge computing processes data nearer to responding to data. Such technologies are in collaborative systems.
1. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
IIoT transforms traditional industrial process control and automation system architectures. These interconnected devices interact across networks without human intervention. Machine-to-machine communication enables autonomous decision-making processes. Predictive analytics predict the failures of equipment weeks prior to their occurrence. Remote diagnostics implies that the visits of technicians to the site would be fewer. The continuous improvement is driven by data-driven insights.

2. Programmable Logic Controllers
PLCs remain the backbone of most control and automation implementations. Modern PLCs offer processing power comparable to desktop computers. They handle complex algorithms while maintaining robust reliability. Programming has become more intuitive with graphical interfaces. Network connectivity allows integration with enterprise systems seamlessly. Their versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications.
3. SCADA Systems
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition enhances industrial controls and automation oversight. SCADA gives one a centralized view of various locations of facilities. Single workstations have thousands of data points monitored by its operators. The analysis of the historical data is used to outline the long-term tendencies. Alarm management provides a rapid reaction to the essential situation. It allows data-driven strategic planning when it is integrated with business systems.
Industrial Control & Automation Implementation Strategies for Facilities
Successful control system automation requires careful planning and execution. Start with an examination of the existing operations. Privatise areas of pain and areas of improvement. Create timetables of gradual implementation so as to reduce disruption in operations. Select chooses technology partners who are of experience in the industry. Make sure that staff training is adequate on all levels.
Assessment and Planning
Every industrial control & automation project starts with thorough evaluation. Document control systems, equipment, and existing processes in totality. objectively compare benchmark performance rates with industry standards. Involve operations, maintenance, and management team stakeholders. Create specific goals and objectives to be measured in terms of success. This foundation will create congruence among business and technology objectives.
System Design Considerations
Effective control and automation design balances multiple competing factors. Scalability guarantees that systems are expanded as new facilities are required. Redundancy will avoid single points of failure of critical systems. The level of cybersecurity protection is in place against even more advanced threats. Easy to use interfaces minimize training and errors. The standardisation eases the maintenance control, spares part inventory is minimised.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Most facilities face challenges integrating new industrial controls and automation technology. Older equipment does not always have new communication features. Protocol converters are used to mediate between old systems and new systems. Gradual replacement procedures retain continuity of production during transitions. With proper planning, there is no interference with the current activities whatsoever.
Industrial Control & Automation Maintenance and Optimization
Control system automation requires ongoing attention to maintain peak performance. Provide regular check-up timeframes of every part of the system. Keep track of the log of the monitor system to determine arising problems in advance. Install updates Software and firmware Updates are issued by manufacturers as improvements are made. Carry out regular operations staff training refreshers. Unremitting optimization assures long-term gains throughout the period of system lifetime.
Predictive Maintenance Approaches
Modern industrial control & automation enables predictive maintenance strategies effectively. Vibration analysis identifies wear on bearings before failure that is catastrophic. Thermal imaging detects electrical faults at an early level. The analysis of oil discloses the internal wear of the hydraulic system. Operating conditions are predicted using statistical algorithms to predict failure probabilities. Such a solution significantly decreases unscheduled downtime cases.
Performance Monitoring
Continuous performance tracking maximizes industrial process control and automation system value. Create key performance indicators that are consistent with business objectives. Easy to understand status of the important measures is displayed as dashboard displays. Trend analysis reveals slow erosion that needs a remedial measure. Compare with past performance to measure gains of improvement. Periodic reviews make sure that systems fit changes in the operations.
Industry Applications
Control and automation serves diverse industrial sectors effectively worldwide. High volumes of production plants are very accurate and throughput rates are higher. The food and beverage operations are used to guarantee uniformity of product. The production of pharmaceuticals has a high level of regulatory compliance. Water purification plants streamline chemical administration and expenditure of energy. Every business manages automation that is industry specific.
Manufacturing Excellence
Manufacturing represents the largest market for industrial controls and automation solutions. Assembly lines organize hundreds of processes with microsecond precision. Quality control systems inspect products at the full speed of the production lines. Logistics systems move components exactly when the process requires them. Scheduling production is based on the automatic adjustment to the real-time demand variations. An outcome of this is efficiency of the manufacturing processes.
Process Industries
Chemical, oil, and gas sectors rely heavily on control system automation. Process control ensures accurate temperature, pressure distribution and flow. The risk systems stop the development of dangerous conditions. Environmental monitoring is applied in order to adhere to regulations on emissions. Complete traceability of the quality can be achieved through batch tracking. These properties are necessary in order to have safe and profitable operations.
Training and Workforce Development
Successful industrial control & automation implementation depends on skilled personnel. New interfaces and procedures must be trained to the operators. Maintenance experts need knowledge in system architecture and system components. The engineers should be up to date with changes in technology standards. The management should have an idea of the capabilities and limitations of systems. All these needs are taken care of through comprehensive training programs.
Operator Training Programs
Effective operator training goes beyond basic system navigation. Simulation environments allow practice without production interruption risks. Scenario-based learning prepares operators for unusual situations. Certification programs validate competency before independent operation begins. Ongoing education keeps skills current with system updates. Well-trained operators maximize automation system benefits significantly.
Technical Skills Development
Maintenance personnel require deep technical knowledge of industrial controls and automation. Troubleshooting skills minimize downtime when problems inevitably occur. PLC programming capabilities enable quick modifications as needs change. Network administration skills ensure robust system communications. Vendor-specific training provides detailed component knowledge. Cross-training creates flexibility within maintenance teams effectively.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation
The industrial control & automation landscape continues evolving rapidly today. Artificial intelligence will enable more autonomous decision-making capabilities. Digital twins will allow virtual testing before physical implementation. Augmented reality will enhance training and troubleshooting effectiveness. 5G networks will enable faster, more reliable communications. Sustainability will drive energy-efficient automation solutions increasingly.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI is transforming control and automation beyond traditional rule-based systems. Machine learning algorithms optimize processes better than manual programming. Pattern recognition identifies quality issues humans might miss completely. Natural language interfaces simplify operator interactions with complex systems. Autonomous optimization adjusts parameters continuously for peak performance. These capabilities will become standard rather than exceptional.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental concerns increasingly influence industrial controls and automation design priorities. Smart grid integration balances energy consumption with availability. Waste heat recovery systems capture and reuse thermal energy. Renewable energy integration optimizes usage of solar and wind. Carbon footprint monitoring enables data-driven reduction strategies. Sustainable automation isn’t just ethical—it’s economically advantageous.
Conclusion
Integrated industrial control & automation isn’t optional for competitive facilities anymore. The technology delivers measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and safety. Modern systems offer unprecedented visibility and control over operations. Implementation requires careful planning but yields significant returns quickly. Future developments promise even greater capabilities and benefits. Facilities that embrace automation position themselves for long-term success.
For over 75 years, IET has delivered comprehensive electrical engineering solutions. Our expertise in industrial control & automation spans Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania. We design, implement, and support systems tailored to your needs. Our team combines technical excellence with deep regional knowledge. Contact IET today to discuss how integrated automation transforms your facility. Let us help you achieve operational excellence through proven solutions.
