If you run mission-critical operations, then you know that the infrastructure must never falter. Facilities where any single downtime can result in millions of losses and damaged reputation require reliable systems in place. These systems help monitor, control, and optimize every process behind the scenes. We are talking about a robust BMS data center.
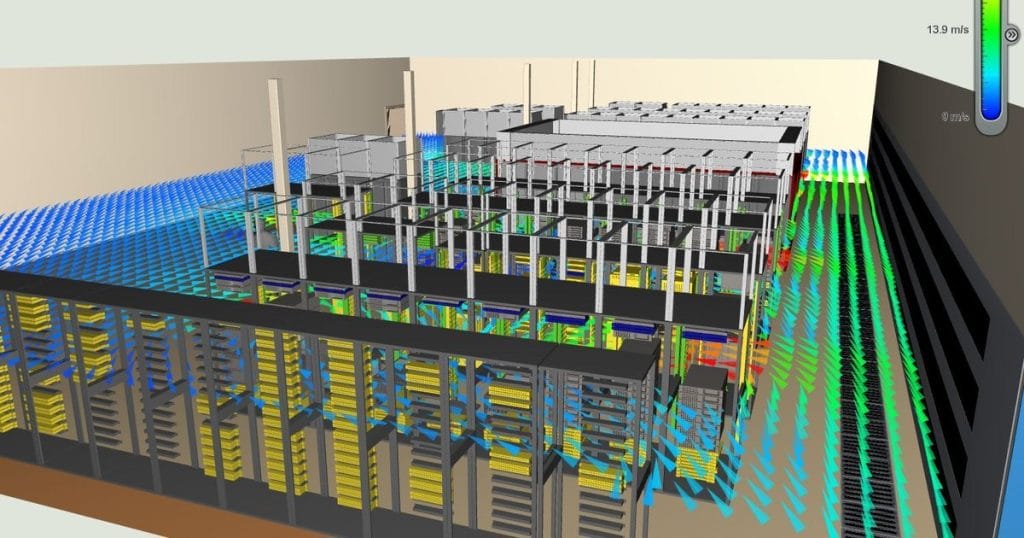
A data center BMS represents the central nervous system of your facility. It controls cooling and power distribution, security and environmental controls. Unlike traditional building management approaches, implementing a data center BMS system addresses the unique challenges of environments where temperature fluctuations of even a few degrees can trigger equipment failures, where power interruptions are simply not an option, and where security breaches carry consequences that extend far beyond the physical facility.
Understanding the Core Functions of BMS in Data Center Operations
The foundation of any effective BMS data center lies in its ability to provide comprehensive oversight across multiple critical systems simultaneously. These are not single monitoring areas placed all over in your facility. Instead, a sophisticated data center BMS creates an integrated ecosystem where every component communicates, responds, and adapts in real-time to changing conditions.
The basic functionality of a BMS in a data center setting is to regulate five areas. The first is the environmental control. Here the system provides improvements in temperature and humidity levels necessary for IT equipment. The second are is power managing that offers effective distribution and redundancy of your infrastructure.
The third area is the security systems that integrates access control, surveillance, and intrusion detection on a single platform. Fourth, automated responses respond to all cooling load changes as well as the use of backup systems in case of anomalies. Fifth, complex data analytics use unprocessed sensor data to create value (statistical insights) to spur continuous improvement.
Real-Time Environmental Monitoring
Temperature management in a data center BMS system goes far beyond simple thermostat control. The sophisticated sensors at every part of the server rooms, cooling units and airflow routes generate finer thermal maps. The building management system data center platform processes this information continuously. The system:
- Identifies hot spots before they become critical
- Adjusts cooling output dynamically
- Predicts equipment stress based on historical patterns
The humidity management is operated in parallel and is able to keep humidity at a level that does not generate condensation damage as well as eliminating the build up of static electricity which may harm delicate electronics.
Power Infrastructure Optimization
Power has not only become the blood of life but also the biggest production cost in most of the facilities. A properly configured data center BMS tracks consumption at granular levels, from individual racks to entire power distribution units. This visibility allows load balancing by ensuring that no one circuit is congested and the amount of unused capacity is exploited.
In case, the utility power supply resorts to failure, the BMS used in data center operation initiates the shift over to uninterruptible power supply and generators and rejects failover chains that ensure uninterrupted process, without operator input.
Integrated Security Architecture
Physical security in a data center BMS system extends beyond traditional access control. Contemporary implementations associate badge access information with surveillance videos, environmental devices and even network activity logs.
When someone enters a restricted area, the BMS data center platform verifies authorization, records the event with timestamp and video evidence, and monitors for unusual patterns that might indicate social engineering attempts or compromised credentials. The security layers resulting through this integration counter the aspects of the appearance of new threats as well as the undisrupted access that authorized personnel need.
Critical Components That Make BMS Data Center Systems Effective
Building an effective data center requires specific hardware and software components working in concert. The central management station is the command center, however, its efficiency solely depends on the quality and position of field devices, the quality of communication networks, and the complexity of control algorithms.
Sensor Networks and Data Collection
A comprehensive BMS in data center installations typically deploys hundreds or even thousands of sensors. Each server rack has temperature probes that check the air temperature both at intake and exhaust points. Moisture sensors monitor the humidity in the facility. The power meters measure power usage, voltage, and current at distribution points.
The airflow sensors maintain that the cooling systems produce the right volumes of cooling air to the heat generating equipment. Physical access is monitored using door contacts and motion detectors. The data center system aggregates this constant stream of data, filtering noise, identifying trends, and flagging anomalies that demand attention.
Control Systems and Automation Logic
Raw data are only of value upon an act. Modern building management system data center platforms employ sophisticated control algorithms that respond to multiple variables simultaneously. In case load on a server surges during business peak hours, the system does not simply pump on the cooling everywhere. Rather, it considers what areas need extra cooling, or can adjust the variable speed fans to achieve accurate volumes of airflow, or can adjust chiller output to match demand, and can even liaise with the power management systems to provide the extra electrical capacity needed by the increased cooling requirements.
User Interfaces and Reporting Tools
Even the most sophisticated data center BMS proves useless if operators cannot access its capabilities effectively. The modern systems offer an array of interface choices, based on particular role and situation. The operators of routine operations can view dashboard displays of the real time status of all systems and the clear visual pointers pointing at the areas of concern.
Facility managers who assess performance trends investigate the history of data using customizable reports that trace the energy efficiency, equipment usage, and maintenance needs, as well as capacity usage. In the incidents, the emergency responders should have user-friendly interfaces that will provide the critical information without reverting to exhaustive details so that they can take swift judgment and make decisions

Assessment and Design Phase
Every effective data center BMS system implementation begins with comprehensive facility assessment. Engineers evaluate existing infrastructure, identifying critical systems, potential failure points, and opportunities for improved efficiency. This assessment informs system design, determining sensor placement, network architecture, control strategies, and integration requirements. The design must accommodate not just current needs but also future expansion, changing technologies, and evolving operational requirements.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Most BMS data center projects involve integrating new management capabilities with legacy systems already in place. This integration presents technical challenges as older equipment may use proprietary protocols or lack the communication interfaces that modern systems expect.
Successful implementations employ gateway devices that translate between protocols, ensuring seamless communication across disparate systems. The data center BMS must also coordinate with infrastructure management platforms, ticketing systems, and other operational tools to provide unified visibility across the entire technology stack.
Testing and Commissioning
Before any BMS in data center goes live, rigorous testing validates every component, connection, and control sequence. Engineers test varying situations, including normal operating modifications, among them, emergencies, to ensure that the system reacts accordingly. The alarm thresholds are adjusted to balance alertness with reality so as not to miss any event and to prevent false alarms which are a confidence ruiner to the operator. Special focus is being given to backup systems; repeat-tests on failover ensure that transitioning automatically is working perfectly on failure of primary systems.
Maximizing Operational Efficiency Through BMS Data Center Analytics
The true power of a modern data center BMS system emerges not from its ability to monitor and control, but from how it transforms operational data into strategic insights. Analytics capabilities turn your data center platform from a reactive monitoring tool into a proactive optimization engine.
Energy Consumption Analysis
The energy expenditures constitute a significant part of the data center operation budget. A sophisticated data center BMS tracks consumption patterns across time periods, correlating usage with factors like server load, outdoor temperature, and operational schedules. Such analyses will create a visibility of opportunities of improvement in efficiency that otherwise could be concealed. It is possible that the cooling systems are used at full capacity during periods when the load on the servers is low. Perhaps there are machines that are inefficient as compared to their counterparts in other facilities. The BMS in data center analytics identify these issues, quantify potential savings, and provide the data needed to justify efficiency investments.
Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
Even when equipment failures avoid actual downtime because they are prevented by redundancy, they cause expensive disruptions. Advanced data center BMS systems employ predictive analytics that identify developing problems before they cause failures. Through the performance when comparing trends on equipment functioning, vibration indicator and power usage, among others, the system identifies units exhibiting early indicators of degradation. Maintenance teams will be able to plan the interventions during premeditated maintenance times, accounted by substituting the components in advance instead of responding to the failures at very essential processes.
Capacity Planning and Optimization
As business needs evolve, understanding available capacity becomes crucial for infrastructure planning. A comprehensive BMS center platform tracks resource utilization across power, cooling, and space dimensions. This visibility enables accurate capacity planning, ensuring you can accommodate growth without over-provisioning expensive infrastructure. The analytics also identify underutilized resources that could support additional load, maximizing return on existing investments before capital expenditures become necessary.
Ensuring Reliability and Resilience in Your Data Center BMS
Reliability cannot be an afterthought when implementing a BMS in data center environments. The management system itself must demonstrate the same uptime and resilience expected from the critical infrastructure it monitors.
Redundancy and Failover Architecture
Leading data center BMS system designs incorporate redundancy at every critical point. Dual network paths ensure communication continues even when primary connections fail. Redundant controllers provide backup processing capacity if primary systems experience issues. Critical sensors deploy in pairs, allowing the BMS data center platform to detect and compensate for sensor failures automatically. Power supplies for management equipment connect to the same uninterruptible power sources protecting IT equipment, ensuring monitoring continues during utility outages.
Security Considerations
A data center BMS represents a potential vulnerability if not properly secured. Such systems are utilized to manage the key infrastructure and gather sensitive working information. It should be implemented by having an effective authentication, encrypted communication, network segmentation of the management traffic with the production networks, and a detailed audit logging on all system accesses and modifications. This also keeps the protection intact as security vulnerabilities are detected through regular security assessments thus preventing threats as threat landscapes change.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Even after successful deployment, a BMS data center requires ongoing attention to maintain optimal performance. System performance, operator feedbacks, trending analysis and periodical testing reviews will ensure that the system remains to meet the operational requirements.
Software updates contain fixes to identified problems and include new features. The configuration changes are made to optimize performance according to experience of operation. This continuous improvement approach keeps your data center BMS system aligned with evolving requirements and emerging best practices.
Partner with Proven Expertise for Your BMS Data Center Implementation
The sophistication required for effective BMS in data center deployments demands partnering with experienced implementers who understand both the technology and the unique operational requirements of mission-critical facilities. It requires expertise that spans all electrical and automation systems and networking as well as data centre operations to be successful.
Having a history of electrical engineering excellence in East Africa over 75 years, IET creates an experience of excellence that is not duplicated in the management of buildings constructed to meet data center and critical facilities needs. Our comprehensive approach encompasses design, implementation, integration, and ongoing support for data center BMS systems that deliver measurable improvements in efficiency, reliability, and operational visibility. From initial assessment through commissioning and beyond, our experienced team ensures your BMS data center investment delivers the performance your operations demand.
Ready to transform your facility management capabilities? Contact IET today to discuss how our building management solutions can optimize your data center operations, reduce costs, and position your infrastructure for future growth.
